The BMS will generate several different study designs. Randomized designs are created via ASreml design engine, a proprietary element of the BMS. When you run a design, the system checks the license via internet. If you experience an error message about a missing license, please contact your system administrator. Checks can be included in study designs (see more about checks under Study Germplasm). The BMS will accept any design via import of design .csv file (see more below).

Design Summary Table
The simplest blocked design is the Randomized Complete Block (RCB) design. In this design each of the v, treatments, occurs once in every block (or replicate), and the number of units per block, k, is constant and equal to the number of treatments (v = k). These characteristics result in a balanced dataset, and therefore, any treatment comparison has the same precision. Treatment factors can be added to RCB designs (see more Treatment Factors).
Select Randomized Complete Block design as the experimental design. Enter the number of desired replications and select Generate Design.
After receiving a success message, the Measurements table is now populated with a randomized complete block design.
In a Resolvable Incomplete block design plots are grouped into blocks that are not large enough to contain all germplasm (treatments). Resolvable blocks are created by grouping incomplete blocks together, so that each treatment is replicated exactly once in each group or set. Number of germplasm cannot be prime. Block size must be greater than 1 and a common denominator of the number of germplasm.
Select Resolvable Incomplete Block Design as the experimental design. Enter the number of desired replications. Enter the blocks size.
After receiving a success message, the Measurements table is now populated with a resolvable incomplete block design.
When the heterogeneity is known or suspected in two directions (rows and columns), Row-and-Column (RC) designs can be used to group experimental units in two directions. The purpose of a RC design is to eliminate equally from the errors all differences among rows and among columns. Under these situations, the experimental material should be arranged and the experiment conducted so that the differences among rows and columns represent major sources of variation. The number of germplasm cannot be prime. The number of rows per replication multiplied by the columns per replication must equal the number of germplasm per replication.
Select Row-And-Column Design as the experimental design. Enter the number of desired replications. Enter the number of row and columns within the replications. Generate Design.
After receiving a success message, the Measurements table is now populated with a Row-and-Column design.
Augmented Randomized Block Design is constructed using control or "check" entries for which there are sufficient seed to allow several replications (see more about checks under Study Germplasm). The number of available experimental plots in each replication may vary, but all of the checks are included at least once; the remaining plots are assigned to the new or "test" entries. Performance of the checks can be used to adjust the performance of the test entries to make them comparable across replications and to provide an estimate of experimental error so that valid statistical tests can be performed. At least one check must be specified. Block number must be a common denominator of the number of test entries.
Specify Augmented Randomized Block Design and enter the number of desired blocks. Generate design.
In this example, there are 2 check entries and 50 test entries. Factors of 50 (1,2,5,10,25) are options for block number in the experimental design.
After receiving a success message, the Observations table is now populated with an augmented randomized block design.
Partially Replicated or P-Rep designs fully replicate check entries and a proportion of test entries in every study instance - thus permitting a limited inventory of test germplasm to be tested over a larger number of environments. Entry type is specified in Studies under the Germplasm & Checks tab. Germplasm designated as a “non-replicated” entry type, will be randomly placed once at each location in a p-rep design. At least one check must be specified. The number of blocks must be a common denominator of the number of plots.
Caution!
P-rep design requires that you manually generate a new design per environment to ensure that different subsets of test entries are selected for every environment.
Enter the percentage of test entries to replicate and the number of replications. Notice that the number of plots is calculated automatically. Enter the number of blocks and generate the design.

Select a single environment. Generate design. Repeat for all environments.

Review the P-rep design in the Observations table.

Error messages appear on the page and in popups to assist you when parameters break the rules of the design.
Adjust the design parameters to proceed. This may involve re-configuring the germplasm list. For example, some designs cannot be generated when the number of test entries per replicate is a prime number.

The number of treatments (test entries) is a prime number, 17. A resolvable incomplete block design can not be generated until the germplasm list is adjusted to a number that is divisible by a number other than 1 and 17.
In this design type the system will read the entry list and assign one plot for each entry in the order established by the list.
Specify "Entry List Order". If your germplasm list has checks (see more about checks under Study Germplasm), you will be asked to specify.
Starting position: where the first check will be inserted (default is plot #1).
Spacing: the number of test entries between check insertion points
Manner of insertion:
Insert each check in turn: will add one check, per insertion point.
Insert all checks at each position: will add the complete list of checks at a given insertion point
After receiving a success message, the Measurements table is now populated with your test and check entries.
This feature allows you to import custom trial design files (.csv) generated outside of the BMS. Randomizations created outside of the BMS may not be supported by BMS statistical analyzes, but users have the flexibility to use external statistics applications if desired.
Export Design Template.
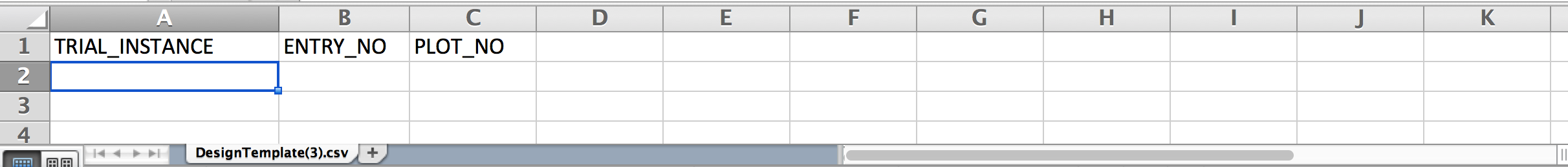
The exported design template (.csv) contains the 3 mandatory column headings
TRIAL_INSTANCE: Number corresponding to specific trial environments, like a particular location or season.
ENTRY_NO: Number corresponding to specific germplasm. The number of entries in the trial design file must equal the number of entries in the trial germplasm list.
PLOT_NO: Plot number
Edit the design template. Some experimental designs will require the addition of other optional columns.
Select Import an Experimental Design.
Specify the design file and Continue.
Terms that are identical to the ontology will map perfectly. If the column headers are spelled differently, the system will attempt to map to match the existing ontology. You may be required to re-map and/or add new ontology terms to achieve correct mapping.

Review imported design details and select Finish.